Class 8 Science Chapter - 3 Coal & Petroleum Notes, Previous Year Questions & NCERT Solutions
Class 8 Science
Chapter - 3
Coal & Petroleum
Notes, Previous Year Questions & NCERT Solutions
--Notes--

Figure 1 Classification of Resources
⏩ Coal, Petroleum and Natural Gas are exhaustible natural resources and are fossil fuels.
⏩ Fossil fuels are fuels that are formed by fossils (dead remains) of living organisms (plants and animals ).
👉 What are fuels?
A fuel is any substance that releases large amounts of energy in the form of heat and light when it is burned. Eg.- coal and petroleum
⏩ Fuels can be classified as:-
| Classification of Fuels | Definition | Examples |
| Solid Fuels | These fuels exist in a solid state at room temperature | For example, coal, firewood, animal dung cakes, charcoal, coke |
| Liquid Fuels | These are volatile liquids that produce vapour which burns and produces energy | For example, petrol, diesel, kerosene |
| Gaseous Fuels | These are the fuels that exist in the form of a gas or as a mixture of different gaseous fuels. | For example, natural gas, biogas, CNG, coal gas |
👉 Why do we need fossil fuels?
Fuels are required for different purposes such as:-
⏩ Transportation: fuels are used to run different vehicles such as cars, trucks, motorcycles, trains, airplanes etc.
⏩ Cooking: fuels are needed for cooking. For instance, LPG is used in urban areas while firewood, coal and cattle dung is used in rural areas.
⏩ Heating: fuel is also used to generate heat
⏩ Electricity production: different fuels such as coal, petrol, natural gas and diesel are used to generate electricity in power plants
⏩ Industrial usage: many industries use fuels for different purposes such as producing electricity, running their machinery and heating
⏩ Rockets and other space vehicles: fuels called propellants are used in rockets that help in launching the space vehicles
👉What are the characteristics of a good fuel?
The characteristics of good fuel are:
⏩ It should be economical and easily available.
⏩ It should not emit poisonous gases on burning.
⏩ It should produce large amounts of heat with respect to its mass (it should have a high calorific value).
⏩ It should be easy to transport and handle.
⏩ It should not produce a bad smell.
⏩ It should be clean and should not produce many ashes.
⏩ It should not ignite/burn easily at room temperature.
👉 Coal:- Coal is a fossil fuel formed from dead plant matter over millions of years due to heat and pressure.
Figure 2 Coal
👉 How is Coal formed?

Figure 3 Formation of Coal
Over millions of years, coal is formed through different biological and geological processes on dead and decaying plant matter.
Coal mainly contains carbon. The process of conversion of dead vegetation into coal is called carbonisation.
What is the composition of coal?
Coal consists of hydrogen, carbon and oxygen and sulphur (small amount).
What is coal mining?
Coal is extracted from the ground with a process called mining. Coal Mining can be of two types:
Opencast Mining: Mining in which coal is extracted from near the earth’s surface
Underground Mining: Mining in which coal is extracted from deep inside the earth’s crust
👉 Different Types Coal
As coal gets older, the carbon content in it is higher. When coal is burnt, it mainly produces carbon dioxide gas.

Figure 4 Types of Coal
👉 Uses of Coal
Used as fuel to cook food.
Used in thermal power plants to produce electricity.
Used as fuel in various industries.
Used as fuel to run steam-powered railway engines.
👉 What is destructive distillation?

Figure 5 Destructive Distillation
It is a process in which coal is heated at very high temperature in the absence of air to obtain various useful products from it. Different products obtained through this process are coal gas, coal tar, coke and liquor ammonia.

Figure 6 Destructive Distillation Process Flow Chart
👉 Major Coal Products

Figure 7 Coal products
👉 What are hydrocarbons?
Hydrocarbons are the substances that consist of only carbon and hydrogen. Compounds like methane, butane, and hexane are hydrocarbons that are produced on burning of the fossil fuels.
👉What will happen if the coal reserves get depleted?
Coal is being used as a major source of energy in industries as well as rural areas.
Not only this, it serves various other purposes like the synthesis of synthetic oil, natural gas, coke, coal tar and coal gas.
If the amount of coal gets depleted it would become much difficult for us to produce energy for various purposes. Hence, we must use coal in an efficient way.
👉What substances are released on the burning of coal?
Carbon dioxide
Carbon monoxide
Sulphur Dioxide
Nitrogen
Lead
Arsenic
Mercury
👉 Petroleum

Figure 8 Petroleum
The term 'Petroleum' is derived from two words - 'Petra' which means 'rock' and 'oleum' which means 'oil'. It is mined from the rocks under the Earth.
Petroleum (also known as crude oil) is a fossil fuel formed from the remains of ancient marine organisms.
👉 How is Petroleum and Natural Gas formed?

Figure 9 Formation of petrol and natural gas
When the sea organisms die, their bodies sink to the bottom of the sea. With time, they get covered by the layers of sand and clay.
Over millions of years, these remains get transformed in petroleum and natural gas due to high temperature, high pressure, and absence of air.
When we dig oil wells, natural gas is above crude oil which in turn is above water. This happens because gas and oil are lighter than water and do not mix with it.
First Oil Well in the World was drilled in Pennsylvania, USA in 1859. Second Oil Well in the World was drilled in Makum, Assam, India in 1867 (after eight years). In India, the oil is found in:
|
👉Refining of Petroleum
Originally, petroleum is a mixture of many things, such as petrol, diesel, paraffin wax, lubricating oil etc.
It is a dark and oily liquid with an unpleasant smell.
Refining of petroleum is the process by which different constituents of petroleum are separated.
👉 Constituents of Petroleum and their Uses

Figure 11 Constituents of Petroleum
👉 Why Petroleum is called ‘black gold?
Petroleum is called 'black god' because it yields several substances that are commercially successful. The useful substances obtained from petroleum and natural gas are called 'petrochemicals'.
Petrochemicals are used in manufacturing:
Synthetic fibres (such as Polyester, Nylon, Acrylic etc.),
Detergents,
Polythene, and
Man-made plastics.
👉 Natural Gas

Figure 12 Natural Gas
Natural gas is a fossil fuel found naturally as a hydrocarbon gas mixture in the oil wells. Its main component is methane but it may also contain varying amounts of other higher alkanes (a group of elements). Gases like carbon dioxide, helium, nitrogen, and hydrogen sulphide are also found in natural gas in small percentages.
👉 Why is Natural Gas important as a fossil fuel?
Natural gas is considered important as this fossil fuel can easily be transported through pipes.
It is stored as CNG which is used for several purposes and is also used as a starting material for manufacturing many chemicals and fertilisers.
Natural Gas does not cause pollution and has high calorific value.
Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) is the natural gas stored under high pressure.
👉 Why is CNG useful?
CNG is used as:
Fuel to generate power
Cleaner fuel for transport vehicles (less polluting than petrol and diesel)
Fuel in homes and industries which can be supplied through pipes.
CNG pipeline network already exists in Vadodara in Gujarat, some parts of Delhi and some other places.
👉 Why is CNG considered as a cleaner fuel?
Natural gas is considered a better fuel than coal and petroleum because it is cleaner.
This means that it results in less amount of pollution that the other fossil fuels.
Natural gas emits 50% less carbon dioxide, sulphur and nitrogen oxides in the air.
However, it is not the best solution as there are better sources of energy present nowadays like solar energy.
In India, vast reserves of natural gas are found in:
|
👉 Some Natural Resources are Limited
Fossil fuels, such as coal, petroleum, and natural gas cannot be created in the laboratory as it is not possible to create the natural conditions under which they are formed. Moreover, it takes thousands of years for them to be formed.
👉 Consequences of the burning of fossil fuels
Increase in air pollution: The burning of fossil fuels results in the release of unburnt carbon particles in the air. These particles act as pollutants and increase air pollution. Fossil fuels release poisonous gases such as carbon monoxide and sulphur dioxide in the atmosphere.
Global Warming: Fossil fuels when burnt release large amounts of carbon dioxide in the air. As the amount of carbon dioxide increases it results in an increase in the global temperature of the earth and leads to global warming.
👉 Why should we use fossil fuels economically?
They are available in limited quantities.
Burning these fuels also cause air pollution as well as global warming.
Hence, we should use these fuels economically to make sure that we can use them for a longer time, the risk of global warming gets reduced, and we can live in a cleaner environment.
--- NCERT Solution ---
Question 1.- What are the advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels?
Answer:- The advantages of using CNG and LPG as fuels are:-
- They burn with a smokeless flame and so does not cause any pollution.
- They leave no ash on burning.
- They are easy to handle and convenient to store.
Question 2.- Name the petroleum product used for surfacing of roads.
Answer:- Bitumen
Question 3.- Describe how coal is formed from dead vegetation. What is this process called?
Answer:- Millions of years ago, trees, plants, ferns and forests got buried below the rocks, soil and sand due to natural processes like flooding, earthquake, etc. Slowly, as more soil deposited over them, they were compressed. This led to the conditions of high pressure and heat. These conditions along with the anaerobic conditions turned the carbon-enriched organic matter of wood into coal.
This slow process of conversion of wood into coal is called carbonisation.
Question 4.- Fill in the blanks.
a) Fossils fuels are ____ , ____ and ____
b) Process of separation of different constituents from petroleum is called ______
c) Least polluting fuel for vehicle is ______
Answer:-
a) coal, petroleum, natural gas
b) refining
c) CNG
Question 5.- Tick True/False against the following statements.
a) Fossil fuels can be made in the laboratory.
b) CNG is more polluting fuel than petrol.
c) Coke is an almost pure form of carbon.
d) Coal tar is a mixture of various substances.
e) Kerosene is not a fossil fuel.
Answer:-
a) False
b) False
c) True
d) True
e) False
Question 6.- Explain why fossil fuels are exhaustible natural resources.
Answer:- Fossil fuels take millions of years to be formed. They are limited in nature and cannot be replenished easily, once consumed. Hence, they are considered as exhaustible natural resources.
Question 7.- Describe the characteristics and uses of coke.
Answer:- Characteristics of coke:- Coke is 98% pure carbon. It is a tough, porous and black substance. It pro-duces a very little smoke.
Uses of coke:- Coke is very useful as fuel. It is a good reducing agent. It is widely used in metallurgical processes to reduce metals from their oxides. It is used for producing water gas.
Question 8.- Explain the process of the formation of petroleum.
Answer:- Petroleum is formed by the burial of aquatic plants and animals below the sea bed. The marine animals and plants died thousands of years ago and settled down in the bottom of sea. In anaerobic conditions, microorganisms decompose this organic matter. Due to high pressure and heat, the dead remains of tiny plants and animals were slowly converted into petroleum.
Question 9.- The following table shows the total power shortage in India from 2004-2010. Show the data in the form of a graph. Piet shortage percentage for the years on the y-axis and the year on the x-axis.
| S. No. | Year | Shortage (%) |
| 1 | 2004 | 7.8 |
| 2 | 2005 | 8.6 |
| 3 | 2006 | 9.0 |
| 4 | 2007 | 9.5 |
| 5 | 2008 | 9.9 |
| 6 | 2009 | 11.2 |
| 7 | 2010 | 10.0 |
Answer:-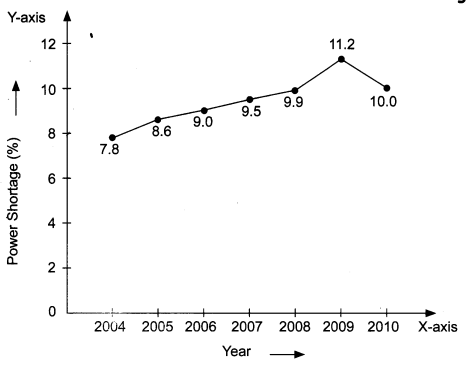
--- Previous Year Questions ---
Question 1.- Define the term fossil fuel. Name two fossil fuels.
Answer:- Fossil fuels are formed from dead remains of living matter over millions of years when they remained buried under the earth. Coal and petroleum are two fossil fuels.
Question 2.- State one use of each of the following :-
- Charcoal
- Bone Charcoal
- Coke.
Answer:- Use:-
- Charcoal : Fuel.
- Bone Charcoal : Purification of brown coloured sugarcane juice in the manufacture of sugar.
- Coke : Used as a reducing agent in the extraction of metals.
Question 3.-
- Name the products obtained when coal is heated in the absence of air.
- Write any two uses of its products. [MSE (Chandigarh) 2007]
Answer:-
- Coke is formed when coal is heated in absence of air.
- Coke is used :
- As a fuel.
- As a reducing agent in the extraction of metals.
Question 4.
a) Give the full form of
i) LPG
ii) CNG
b) How is petroleum gas obtained ? [MSE (Chandigarh) 2007]
Answer:-
a) i) LPG — Liquefied Petroleum Gas.
ii) CNG — Compressed Natural Gas.
b) Petroleum gas is obtained during fractional distillation of petroleum.
Question 5.- Draw diagram to show petroleum and natural gas deposit.
Answer:-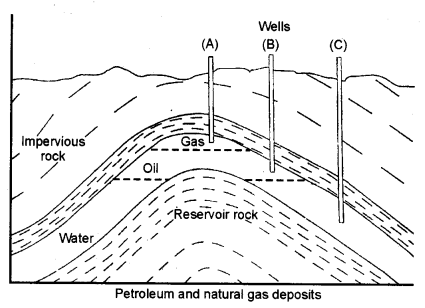
Question 6.- What are ‘Petrochemicals’ ? Give the uses of petrochemicals obtained from petroleum.
Answer:- Petrochemicals are useful substances obtained from petroleum. They are used in the manufacture of detergents, fibres, polyethylene and other plastics.
Question 7.- Name some places where natural gas is found in India. How many reserves are of natural gas ?
Answer:- In India, natural gas has been formed in Tripura, in the Krishna Godavari delta. In India, there are over 100 billion cubic metre reserves of natural gas.
Question 8.- Describe characteristics and uses of coke.
Answer:- Characteristics of coke are :
- it is tough.
- it is porous
- it is pure form of carbon.
Coke is used for extraction of metals and in the manufacture of steel.
Give Us Your Feedback/Suggestions
- By Durgesh Pandey
(Eklavya Coaching Institute)
📞 8376976688, 9310533915
H-2/25, Gali No-23, Kunwar Singh Nagar, Nangloi, New Delhi -110041







Comments
Post a Comment