Class 8 Science Chapter - 6 Combustion & Flame Notes, Previous Year Questions & NCERT Solutions
Class 8 Science
Chapter - 6
Combustion & Flame
Notes, Previous Year Questions & NCERT Solutions
--Notes--
👉What is Combustion?
➧Combustion is a chemical process in which a substance reacts with oxygen and generates heat in the process.
➧Combustible substances are those substances that undergo combustion. It means that these substances give off heat and sometimes light (as a flame or glow) when they react with oxygen.
➧Inflammable substances are substances which have low ignition temperature and catch fire easily. They burn with a flame. For example, petrol, LPG etc.
➧Why do we say that food is fuel for our body?
When we eat food, it gets broken down in simpler substances which react with oxygen and generate energy (or heat). Hence, food is referred to as ‘fuel’ for our body.
👉 Conditions necessary for the Combustion to take place are:
➧Combustion requires fuel.
➧Combustion requires air. A candle keeps burning in open air. However, when we cover it with a glass or a jar, it only burns until the oxygen inside it is consumed. Once the oxygen is exhausted, the flame of the candle flickers off.
➧Combustion requires heat.
The substance must reach its ignition temperature to catch fire. |
➧Ignition temperature is the lowest temperature at which a substance catches fire or starts burning.

Types of Combustion
Rapid Combustion: Combustion in which a gas burns quickly producing heat and light in the process. E.g. LPG
Spontaneous Combustion: Combustion in which a material bursts into flames suddenly without applying heat. E.g. Phosphorus which burns at room temperature.Spontaneous combustion of coal dust often causes accidental fires in coal mines. Heat from the sun or lighting may also cause spontaneous forest fires.
Explosion: When a material bursts suddenly to produce heat, light and sound on the application of heat or pressure, it is called an explosion. E.g. Crackers and fireworks which release a large amount of gas too.
How do We Control Fire?
We can control the fire by one or more of the following:
Removing the fuel
Cutting off the air supply (or oxygen supply)
Cutting off heat or lowering the temperature of the fuel
How do fire extinguishers work?
Fire extinguishers are devices used to put out fires. They either cut off the air supply to fire or cool off the fuel (below the ignition temperature) or both. The three main types of fire extinguishers are:
‘Dry Powder’ Fire Extinguisher: This type of fire extinguishers contain a mixture of baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) and sand. When you throw it over the fire, the baking soda decomposes by its heat to produce carbon dioxide. Since CO2 is heavier than air, it descends to envelop the burning flame and cuts off its contact with air (and the oxygen supply).
2NaHCO3 → Na2CO3 + H2O + CO2
‘Soda-acid’ Fire Extinguisher: This fire extinguisher is a metallic cylinder which contains the sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) solution. At the bottom of the cylinder, the concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4) is placed in a thin sealed glass tube. A fixed wire gauze surrounds this tube.

Below the tube, a plunger is placed with its sharp end touching the thin glass tube.
On the top of the cylinder, there is a nozzle which is sealed with wax.
When the plunger hits against the floor, its sharp end breaks the thin glass tube and the acid inside it reacts with sodium bicarbonate to produce carbon dioxide. CO2 forces the wax seal open and rushes out of the nozzle to put out the fire in the direction where the nozzle is pointed.
‘Foam-type’ Fire Extinguisher: Like the soda-acid fire extinguisher, it uses sodium bicarbonate solution. However, in this case, a substance called Saporin or Turkey Red Oil is added to the solution to produce foam along with the gas from the nozzle. Since this foam is lighter than oil, it floats on the surface of the oil and cuts off its air supply. Hence, it is very effective in putting out oil fires.
When should we use (or not use) water to extinguish the fire?
When wood, paper and clothes are on fire, we can use water to extinguish them. Water lowers the temperature of burning material below ignition temperature and thus, the fire stops burning.
We should not use water when electrical equipment is on fire as water may conduct electricity and give a shock to people dousing the fire. Also, it should not be used when oil or petrol catches fire as water is lighter than oil and petrol and sinks down. Oil and petrol keep floating on the top and keep burning.
What should we do when electrical equipment or inflammable materials (like petrol) catch fire?
Carbon Dioxide is the best fire extinguisher in such cases. CO2 is heavier than oxygen and hence, covers the burning material like a blanket and cuts off its oxygen supply. Also, it does not harm the electrical equipment.
CO2 can be stored as a liquid in cylinders at high pressure. When it is released, it immediately expands, cools down, and envelopes the fire - bringing down the temperature of the fuel. One can also pour dry chemicals like sodium bicarbonate (or baking soda) or potassium carbonate on the fire as they release CO2 near a fire.
Flame
Flame is a hot glowing body of ignited gas which is produced when something is on fire.
Some materials burn with a flame and some do not. Here is a table based on a general observation:
Materials forming Flame on Burning
| Material | Forms flame | Does not form a flame |
| Candle | Forms flame | |
| Magnesium | Does not form a flame | |
| Camphor | Forms flame | |
| Kerosene Stove | Forms flame | |
| Charcoal | Forms flame |
Structure of a Flame

A flame has three zones:
➧Outermost zone is blue in colour and is the hottest part of the flame. This is also the zone where complete combustion takes place.
➧Middle zone is yellow in colour and is moderately hot. In this zone, partial combustion takes place.
➧Innermost zone is black in colour and least hot. Here, we can find the unburned wax vapours of a candle.
Note:- Kerosene oil and molten wax vapourise during burning but charcoal does not produce flame or vapourise when it burns.
➧Why do goldsmiths blow at the outermost zone of a flame for melting gold and silver?
The outermost zone of a flame is its hottest part. Gold and silver have high melting points and hence, goldsmiths blow at the outermost zone of the flame to melt gold and silver quickly.
What is a Fuel?
Fuels are substances that give us heat which we use for domestic and industrial purposes, such as wood, kerosene, and petrol.
➧What will an ideal fuel or good fuel look like?
Ideally, a good fuel is one which:
has proper ignition temperature (neither too high nor too low),
does not produce undesirable or poisonous substances and cause pollution,
does not leave behind much ash,
is cheap,
is readily available,
produces a large amount of heat or have high calorific value,
has a moderate rate of consumption,
is easily controllable (can be started or stopped as needed),
is easy to handle and transport, and
has low moisture content (so that it burns easily).
Fuel Efficiency
➧Fuel efficiency of a fuel depends on its calorific value.
➧The calorific value of a fuel depends on the amount of heat produced by complete combustion of 1 kg of the fuel. The unit used to measure the calorific value of a fuel is kilojoule per kg (kJ/kg).
Calorific Value of Common Fuels We Use

If we look at the table, we will see that hydrogen seems to be the most efficient fuel followed by LPG. CNG and Methane come next, closely followed by Kerosene, Diesel and Methane. Cow dung cake seems to be the least efficient fuel here.
Uses of Fuels
Some of the ways in which common fuels are used are:
Gasoline is used in cars, scooters and other vehicles we use every day.
Natural gas is used in heating systems, water heaters, dryers, and stovetops in our homes.
Oil and natural gas are used in making several things that we use every day. Hydrocarbons, for example, are used in making plastics, pharmaceuticals and several other items we use daily.
Coal is the primary fossil fuel used in many thermal power plants to produce electricity.
Types of Fuels
Fuels can mainly be divided into three groups:
Liquid Fuels: Petroleum (which is a fossil fuel), crude oil (from which we get petrol or gasoline), diesel, kerosene oil etc.
Solid Fuels: Firewood, charcoal, coal (fossil fuel which is mined as steam coke or soft coke), dung cakes, tallow (animal fat), straw and other agricultural wastes, paraffin wax, camphor etc.
Gaseous Fuels: Most commonly used gas is LPG (Liquid Petroleum Gas) which we use as cooking gas at home. Some of the other commonly used gaseous fuels are:
We get CNG (Compressed Natural Gas) from natural oil wells.
Natural gas (or methane) gets released from the putrefying organic matter.
Butane gas is obtained from natural gas.
In the villages, animal dung and farm waste are used to produce biogas. Biogas is also collected from sewage plants.
When hard coke is heated and converted into coke, coal gas is produced.
Water gas is produced by passing steam over red-hot coke.
Acetylene used a gas produced by adding calcium carbide to water. Its smell is a bit unpleasant but the flame it produces is so hot that it is used for cutting metals and welding purposes.
Harmful Effects of Burning Fuels
Carbon fuels like wood, coal and petroleum release ash and fine unburnt carbon particles in the air which can cause respiratory diseases like asthma. These fine particles are referred to as Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM).
Incomplete combustion of fuels (such as coal, gasoline and other fossil fuels) releases carbon monoxide gas which is very poisonous and can kill people sleeping in the room where coal is burning. CO combines with haemoglobin in our blood to form carboxyhemoglobin and renders it incapable of transporting oxygen. These fuels also release unburnt hydrocarbons, many of which are carcinogenic (cause cancer) and pose serious health hazards.
Carbon dioxide released by most fuels during combustion is causing an imbalance in the atmosphere. Deforestation is also leading to a situation where there are fewer trees to absorb the carbon dioxide. This is leading to global warming.
Burning of coal and diesel releases sulphur dioxide gas which is corrosive in nature and causes irritation in nose, throat and airways. It also causes shortness of breath, wheezing, and a feeling of tightness around the chest. Petrol engines release gaseous oxides of nitrogen. These sulphur and nitrogen oxides dissolve in rainwater to form acids and cause acid rain.
Global warming is the rising temperature of the Earth's atmosphere which is causing the melting down of glaciers making the sea levels rise and causing floods in coastal areas. It is caused due to the elevated levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere as CO2 absorbs infrared radiation emitted by the Earth and radiate it back to the atmosphere and raise its temperature. This is also known as the ‘greenhouse effect’. Acid Rain refers to the rain of acids that is very harmful to crops, soil, animals, and buildings. These acids are formed when sulphur and nitrogen oxides dissolve in rainwater. Acid rains also damage trees at high elevation (such as red spruce that grows 2,000 ft above sea level), causes acidification of lake or stream water, and damage forest soils. Irreplaceable buildings, statues and sculptures which are part of a nation’s cultural heritage can get destroyed due to acid rain. |
Why do we not burn wood anymore?
Wood is a low-cost fuel and is easily available but burning it releases a lot of smoke which causes respiratory problems. Moreover, cutting of trees for wood (as fuel) also leads to deforestation. Hence, people now prefer to use coal or LPG as fuel instead.
Why should we use CNG as automobile fuels?
CNG is a cleaner fuel and causes much less pollution than petrol and diesel. Hence, we should use CNG-powered vehicles now.
How to Conserve Fuels?
To conserve fuels, we should:
Collect all material required while cooking at one place before switching on the gas,
Check the pressure of tyres regularly,
Choose walking over using cars or motorbikes for short distances, and
Use public transportation for travelling instead of private vehicles.
----- NCERT Solution -----
Question 1.- List conditions under which combustion can take place.
Answer:- Combustion can take place in the presence of:
a) a combustible substance.
b) oxygen, that is, the supporter of combustion.
c) attainment of ignition temperature of the substance.
Question 2.- Fill in the blanks.
a) Burning of wood and coal causes _____ of air.
b) A liquid fuel, used in homes is ______
c) Fuel must be heated to its ______ before it starts burning.
d) Fire produced by oil cannot be controlled by ______
Answer:- a) pollution
b) LPG
c) ignition temperature
d) water
Question 3.- Explain how the use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities.
Answer:- The use of CNG in automobiles has reduced pollution in our cities as it is a quality fuel and has some benefits:
a) It gives out less carbon dioxide gas, carbon monoxide gas, sulphur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide, which is beneficial as they play crucial role in global warming and acid rain.
b) It leaves behind no residue after its combustion.
Question 4.- Compare LPG and wood as fuels.
Answer:-
| LPG | Wood |
| i) It does not cause pollution on combustion. | i) It pollutes air on its combustion. |
| ii) No smoke is produced. | ii) It produces smoke. |
| iii) It is a liquid fuel. | iii) It is a solid fuel. |
| iv) It has more calorific value (55000 kJ/kg). | iv) It has less calorific value (17000 kJ/kg). |
| v) It can be easily transported, as it is stored in cylinders. | v) It can’t be transported easily like LPG fuels. |
Question 5.- Give reasons.
a) Water is not used to control fires involving electrical equipment.
b) LPG is a better domestic fuel than wood.
c) Paper by itself catches fire easily whereas a piece of paper wrapped around an alluminium pipe does not.
Answer:-
a) Since water is a good conductor of electricity, it may result in electric shocks to the person trying to extinguish fire.
b) LPG is better domestic fuel than wood because it does not produce gases, nor does it leave any residue behind. Moreover, it has more calorific value than wood.
c) As its ignition temperature is low, the paper by itself catches fire easily. But a piece of paper wrapped around an alluminium pipe does not catch fire easily, as the heat being given gets absorbed by the alluminium pipe and the piece of paper does not get its ignition temperature.
Question 6.- Make a labelled diagram of a candle flame.
Answer:-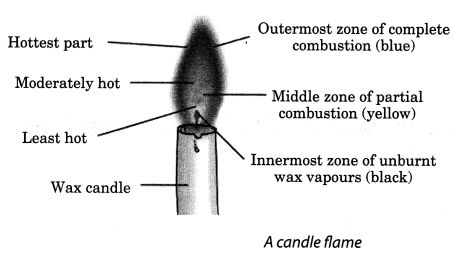
Question 7.- Name the unit in which the calorific value of a fuel is expressed.
Answer:- The unit in which the calorific value of a fuel is expressed is kilojoules per kilogram (kJ/kg).
Question 8.- Explain how CO₂ is able to control fires.
Answer:- As CO₂ is heavier than oxygen, it forms a blanket around fire, because of which the supply of air is stopped. Men over, it brings down the temperature of the burning substance. In these ways, it plays a significant role in controlling fire.
Question 9.- It is difficult to burn a heap of green leaves but dry leaves catch fire easily. Explain.
Answer:- The green leaves hold some amount of water, so its ignition temperature gets increased and it does not burn easily. On the other hand, dry leaves are waterless, so they catch fire easily (having low ignition temperature).
Question 10.- Which zone of a flame does a goldsmith use for melting gold and silver and why?
Answer:- A goldsmith uses the outermost zone of a flame, which is non-luminous, to melt gold and silver as it is the hottest zone of the flame, having more temperature.
Question 11.- In an experiment, 4.5 kg of a fuel was completely burnt. The heat produced was measured to be 180,000 kJ. Calculate the calorific value of the fuel.
Answer:- Calorific value of a fuel =
=
= 40,000 kJ/kg.
Question 12.- Can the process of rusting be called combustion? Discuss.
Answer:- The process of rusting emits heat during the formation of its oxide. So we can call the process of rusting as slow combustion.
Question 13.- Abida and Ramesh were doing an experiment in which water was to be heated in a beaker. Abida kept the beaker near the wick in the yellow part of the candle flame. Ramesh kept the beaker in the outermost part of the flame. Whose water will get heated in a shorter time?
Answer:- The water which was put by Ramesh will get heated in a shorter time; because he had put it nearer to the hottest zone of the flame.
----- Previous Year Questions -----
Question 1.
- Name the type of nuclear reaction taking place in the atmosphere of Sun.
- Define ignition temperature.
- Why water should not be used to put out fire caused by burning of petrol. [MSE (Chandigarh) 2008]
Answer:
- Nuclear fusion.
- The minimum temperature to which a substance is heated before it starts burning is known as ignition temperature.
- Petrol is lighter than water, so it floats on top of water and continuous burning. So, it cannot be used for extinguishing fire due to burning of petrol.
Question 2.
Give two examples each of solid fuel, liquid fuel and gaseous fuel. [KVS 2008]
Answer:
- Solid fuel — coal, wood
- Liquid fuel — petrol, kerosene
- Gaseous fuel — LPG, methane
Question 3.
Write any four characteristics of an ideal fuel. What is C.N.G. ? Mention its one use. [DAV2005]
Answer:
- It is cheap and easily available. ,
- It does not produce any harmful gas during burning.
- It has high calorific value.
- It is safe and easy to store.
C.N.G – Compressed Natural Gas. It is used as a fuel for automobiles.
Question 4.
Explain the different zones of a flame with the help of a neat and well labelled diagram.
Answer:
- The innermost zone is the dark zone. It contains unburnt vapours of wax.
- The second zone is the yellow zone where incomplete combustion takes place. It is known as luminous zone.
- The thin outermost zone of the flame is blue in colour and complete combustion takes place. This is the non-luminous zone.
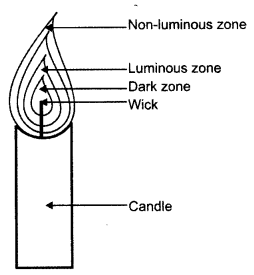
Question 5.
- Which is the hottest zone and the coolest zone of a flame ?
- Why does the middle zone of the candle flame glow with yellow colour ?
Answer:
- The innermost or dark zone has minimum temperature. The outermost or non-luminous zone has maximum temperature.
- In the middle zone, the unburnt carbon particles give the flame its yellow colour.
Question 6.
Why do we use paper or kerosene oil to start fire in wood or coal ?
Answer:
The ignition temperature of wood or coal is very high. So, we bum paper or kerosene oil to provide large amount of heat, as they have a low ignition temperature.
Question 7.
Explain how water extinguishes the fire.
Answer:
Water cools the combustible material so that its temperature is brought below its ignition temperature. Water vapours also surround the combustible material, helping in cutting the supply of air. So, the fire is extinguished.
Question 8.
How does the foam type fire extinguisher work ?
Answer:
At airports and petrol pumps, the foam type fire extinguisher is used which is based on the principle of smothering the fire. In this extinguisher, sodium bicarbonate contains Turkey red oil. When it is operated, carbon dioxide liberated in reaction of dilute sulphuric acid with sodium bicarbonate comes out under pressure in the form of a foam and settles on the fire.
Question 9.
You are given three substances A, B and C. How will you find out which of them as a combustible material ?
Answer:
He will bum each substance with the help of match stick. If it bums it is a combustible substance and if it does not bum it is a non-combustible substance.
Question 10.
When the clothes of a person catches fire, we cover him with a blanket. Why ?
Answer:
When the person is covered with a blanket, the supply of oxygen is cut off. So, the fire is put off.
Question 11.
Red buckets containing sand are kept in offices and cinema halls. Why ?
Answer:
These are kept so as to extinguish the fires. When there is a fire, sand is thrown on it, so as to cut off the supply of oxygen.
Question 12.
What is the function of a wick in the candle ?
Answer:
The wick draws up the molten wax, which than bums to form a flame.
Give Us Your Feedback/Suggestions
- By Durgesh Pandey
(Eklavya Coaching Institute)
📞 8376976688, 9310533915
H-2/25, Gali No-23, Kunwar Singh Nagar, Nangloi, New Delhi -110041




Comments
Post a Comment