Class - 9 Science (Chemistry) Chapter - 1 Matter in Our Surroundings Notes, Ncert Solutions & Frequently Asked Questions -- Notes --
Class - 9
Science (Chemistry)
Chapter - 1
Matter in Our Surroundings
Notes, Ncert Solutions & Frequently Asked Questions
-- Notes --
⭐ What is Matter?
-- Air, water, stones, sand, clouds, pencils, books – Everything is made up of matter. Matter is everything in this universe that occupies space and has mass.
⭐Constituents of Matter:- According to the early Indian philosophers, every living and non-living thing is made of five basic elements called the Panchtatva – Air, Water, Earth, Sky, and Fire. Therefore, matter is a composition of these five constituents.
⭐ Physical Nature of Matter:-
Is matter continuous or particulate?
• Matter is particulate in nature. Matter is made up of tiny particles.
• For Example, If we put a drop of red colour in water the colour of the water turns red. This happens because the particles of red colour mix with the particles of water.
⭐ What is the size of these particles?
• The size of the particles of matter is very small.
• They can be broken into further particles as well.
• For Example, On dilution of a colourful solution, we can still see the colour.
• This means there are millions of particles present in the colour which just divide themselves on dilution.
⭐ Characteristics of Particles of Matter:- Particles of matter have three characteristics:-
a) Particles of matter have spaces between them
⏩ What causes salt to get dissolved in water?
• Salt gets dissolved in water because its particles have spaces between them. The particles of the salt get in between the spaces between the particles of water and a mixture is formed. We cannot see these particles through naked eyes.
b) Particles of Matter are continuously moving
• Particles of matter are in motion all the time. Hence, they possess kinetic energy.
• Kinetic Energy = Energy due to motion
• The particles of a matter intermix on their own with other particles of a matter.
• Diffusion – The process of mixing two different types of particles together is called diffusion. Diffusion becomes faster on heating.
• The kinetic energy of particles also increases on heating.
c) Particles of Matter attract each other
• The particles of matter are always held together because of a force of attraction between them.
• The amount of this force between the particles varies in different forms of matter.
• Solids have the highest force of attraction. That is why we cannot move our hands through a solid object. The particles are so tightly bound.
• Similarly, particles of gases have the least force of attraction in them. We can move our hands easily in the air. This is because the particles of air are loosely bound.
• Force of attraction between different types of matter (solids, liquids, and gases) in increasing order:- Gas < Liquid < Solids
• We can also move our hands through water or liquid matter but not as freely as we can in the air. This means that they are also loosely bound to some extent.
⭐ States of Matter:-
• Particles of matter have a force of attraction between them. Based on this criterion, matter is present in three different states:- solid state, liquid state, and gaseous state.
a) The Solid State:- Solids are the objects that have these three properties:
-- They have a specific shape.
-- They have distinct boundaries.
-- They have a volume.
• There is less kinetic energy among the particles in solids. They are generally arranged in order. Thus they possess a fixed shape. They cannot be compressed.
• The force of attraction is the maximum among the particles of solids. There is not much space between the particles. Therefore, they cannot be compressed.
⏩ Which of these are solids:- Rubber band, Sponge, Salt?
All of them are solids. All of these follow the properties of solids. A rubber band and sponge change their shape only when we apply force on them. It might appear to you as if salt is taking the shape of the container in which you put it but actually each grain has its own definite shape.
b) The Liquid State:- Liquids have the following properties:-
-- Liquids have a fixed volume
-- Liquids do not have a fixed shape.
• The force of attraction in liquid particles is less than in solids. Therefore, there is a space between the particles of liquids and they can flow easily. They cannot be compressed. That is why they are also called fluids.
• Particles of liquids arrange each other and are not fixed. You might have seen that liquids take the shape of the container in which we put them. This is because the particles of liquids have high kinetic energy, they always keep on moving.
⏩ Can other matter diffuse into liquids?
Yes, other matter can diffuse into liquids whether it is solids, liquids, or gases. This is so because there is a space between the particles of liquid so particles of other matter can slip into those spaces.
-- Diffusing solids into liquids:- Mixing sugar in tea
-- Diffusing liquids into liquids:- Mixing ink in water
-- Diffusing gases into liquids:- The presence of oxygen and carbon dioxide in water
c) The Gaseous State:- Gases have the following properties:-
-- They do not have a fixed volume.
-- They do not have a fixed shape.
• The particles of gases have the least or almost no force of attraction between them. Therefore, the particles have a large number of spaces between them and they can freely move in any direction.
• Also, they can be easily compressed and put into a small container, unlike solids and liquids.
• Since there is a lot of space between the particles, different gases can diffuse into each other easily.
• The kinetic energy between the particles is the maximum in the case of gases. Therefore, the particles move around freely at high speed and there is no fixed shape of gases.
⭐ The difference in the characteristics of states of matter:-
⭐ Can Matter Change its State?
Water exists in three states:-
• Ice – solid
• Water – liquid
• Water Vapour – Gas
This is an indication that matter can change its states.
⭐ Effect of Change of Temperature:-
What happens to matter when we heat it?
a) Solids:- As we heat solids, the kinetic energy between the particles of solids increases which decreases the force of attraction between them.
• They start vibrating and changing their positions. Slowly, due to heat the particles become free and a solid converts into liquid.
• Melting Point – The temperature at which solid melts to become a liquid at atmospheric pressure. For Example, the melting point of ice is 273.16 Kelvin.
• Fusion – The process of melting a solid into liquid is called Fusion.
• In the melting process, once a solid reaches its melting point, its temperature does not increase further. So where does all the heat go? The heat present in the solid at the time of melting is used by the particles to diminish the force of attraction between each other. The heat energy is therefore considered hidden.
• Latent Heat – The heat energy which is used to break the force of attraction between the particles of matter is known as latent heat. Since the heat is hidden therefore it is called Latent Heat.
• Latent Heat of Fusion – The amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of a solid into liquid at atmospheric pressure at its melting point is known as the Latent Heat of Fusion.
• Atmospheric Pressure – Pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere.
b) Liquids:- Just like in solids, the kinetic energy of particles of liquid increases, the force of attraction among them decreases and they start moving freely.
• As we keep on supplying the heat, a point comes when the particles overcome the forces of attraction completely.
• This is when a liquid starts changing into gas.
• Boiling Point:- The temperature at which a liquid starts boiling at the atmospheric pressure is known as its Boiling Point. For Eg.- The boiling point of water is 373 Kelvin.
• Latent Heat of Vaporisation:– the amount of heat energy required to change 1 kg of a liquid into a gas at atmospheric pressure at its boiling point is known as Latent Heat of Vaporisation.
What happens when we decrease the temperature?
a) Gases:- The kinetic energy between the particles decreases and they turn into a liquid state.
• Condensation / Liquefaction – The process of converting gas into a liquid by cooling down its temperature. For Example, The formation of clouds is due to the condensation of water vapour from Earth.
b) Liquids:- The kinetic energy between the particles decreases and they turn into a solid-state. For Example, The formation of ice.
• Sublimation – change of state of gas directly into solid and vice-versa is known as sublimation. For Example, Camphor is a solid that directly evaporates into the air without changing to a liquid state.
• Therefore, by increasing or decreasing the temperature we can change the states of matter into one another.
⭐ Effect of change of Pressure:- By applying pressure, we can bring the particles of matter close to each other thereby, increasing the force of attraction among the particles.
• When we compress and decrease the temperature of a gas, the gas changes into a liquid.
• Dry Ice – Carbon dioxide in solid form is known as Dry Ice. It can directly turn into a gas by decreasing the pressure to 1 atmosphere.
⭐ Evaporation:- We already know that –
• Particles of matter are never at rest
• Particles of matter possess different amounts of kinetic energy
• The particles of liquids have more kinetic energy. Therefore, they are able to overcome the forces of attraction and convert into vapour without any external forces.
• The phenomenon of change of a liquid into vapours at any given temperature below its boiling point is called Evaporation. Evaporation is different from boiling, as shown in the figure below.
⭐ Factors Affecting Evaporation:-
⭐ How evaporation causes cooling?
• The process of evaporation uses the energy of the liquid particles. Therefore, the particles absorb energy from the surroundings in order to compensate for the energy that is being lost in the process of evaporation. This results in the cooling of the surrounding area.
• For Example:-
-- Our palms feel cool when we put some acetone (nail paint remover) on it.
-- People sprinkle water on their roofs or ground on sunny days to cool the area.
-- We are able to sip hot tea faster in a saucer than in a cup.
⭐ Why do people wear cotton clothes in summer?
• We sweat more in summer. As the sweat evaporates it takes energy from our body surface and keeps our body cool. Cotton can absorb the sweat easily and exposes it to the atmosphere causing evaporation to take place easily. This, in turn, keeps us cool on summer days.
⭐ Why do water droplets appear in the surroundings of glass with ice-cold water?
• There are water vapours present in the air. When they come in contact with the walls of the glass that has ice-cold water in it they condense. As a result, their state changes from the gaseous state to liquid state thus forming tiny water droplets on the walls of the glass.
⭐ The Five States of Matter:- We have discussed the three states of matter – Solid, Liquid, Gas.
• But, scientists have discovered that there are two more states of matter -
• Plasma:- It is a state of matter in which the particles are super excited and super energetic. They are in the form of ionised gases.
-- For Example – Fluorescent tubes and neon light bulbs consist of plasma
-- The neon bulbs contain neon gas and there is another gas such as helium in the fluorescent tube. As electricity is passed in the tube or the bulb, these gases get ionised and this creates the plasma inside them that glows.
-- In fact, the Sun and the stars glow because plasma is present in them.
• Bose-Einstein Condensate (BEC):- It is the fifth state of matter discovered by Albert Einstein based on the studies conducted by an Indian scientist Satyendra Nath Bose.
-- BEC is formed by condensing gases of extremely low densities to much lower temperatures.
⭐ Important Measurement Units:-
-- NCERT Solutions --
Intext Questions (Page: 3)
Question 1.- Which of the following are matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, lemon water, the smell of perfume.
Solution:- The following substances are matter:- Chair, Air, Almonds, Lemon water & the smell of perfume.
(Smell is considered as a matter due to the presence of some volatile substances in air that occupy space & have mass.)
Question 2.- Give reasons for the following observation:-
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several meters away, but to get the smell from cold food, you have to go close.
Solution:- Particles in the air, if fueled with higher temperatures, acquire high kinetic energy, which aids them to move fast over a stretch. Hence, the smell of hot sizzling food reaches a person even at a distance of several meters.
Question 3.- A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
Solution:- The diver is able to easily cut through the water in the swimming pool because of the weak forces of attraction between water molecules. It is this property of water that attributes to easy diving.
Question 4.- What are the characteristics of the particles of matter?
Solution:- The characteristics of particles of matter are as follows:
a) Presence of intermolecular spaces between particles
b) Particles are in constant motion
c) They attract each other
d) All matter is composed of very small particles which can exist independently.
Intext Questions (Page: 6)
Question 1.- The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density. (density=mass/volume). Arrange the following in the order of increasing density – air, exhaust from the chimneys, honey, water, chalk, cotton and iron.
Solution:- The following substances are arranged in increasing density:
Air < Exhaust from chimney < Cotton < Water < Honey < Chalk < Iron
Question 2.- Answer the following.
a) Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of matter.
Solution:-
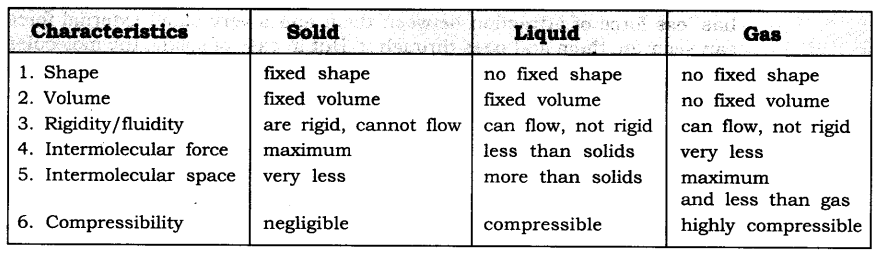
b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy and density.
Solution:-
i) Rigidity: It is the property of matter to continue to remain in its shape when treated with an external force.
ii) Compressibility: It is the attribute of the particles to contract their intermolecular space when exposed to an external force, thereby escalating its density.
iii) Fluidity: It is the ability of a substance to flow or move about freely.
iv) Filling the gas container: The particles in a container take their shape as they randomly vibrate in all possible directions.
v) Shape: It is the definite structure of an object within an external boundary
vi) Kinetic energy: Motion allows particles to possess energy which is referred to as kinetic energy. The increasing order of kinetic energy possessed by various states of matter are:-
Solids < Liquids < Gases
Mathematically, it can be expressed as , K. E. = 1/2 mv² where ‘m’ is the mass and ‘v’ is the velocity of the particle.
vii) Density: It is the mass of a unit volume of a substance. It is expressed as:
d = M/V, where ‘d’ is the density, ‘M’ is the mass and ‘V’ is the volume of the substance
Question 3.- Give reasons:-
a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
Solution:- There is a low force of attraction between gas particles. The particles in the filled vessel are free to move about.
b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
Solution:- Gaseous particles have the weakest attraction force. They are always moving in a haphazard manner. When a gas particle collides with the container’s walls, it exerts force and, thus pressure on the wall.
c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
Solution:- There is a distinct contour and volume to the hardwood table. The wood particles are tightly packed. They do not conform to the container’s shape. As a result, the solid features of a hardwood table are satisfied.
d) We can easily move our hand in the air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Solution:- The boundaries between air particles are quite loose. They are a long way apart and have a lot of space between them. As a result, we may move our hands freely in the air. The particles in a solid block, on the other hand, are bound together by a strong force of attraction. As a result, there is either some or no space between them. As a result, we will require a karate expert.
Question 4.- Liquids generally have a lower density than solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
Solution:- In general, the volume of a liquid is more than the volume of a solid because liquid particles are freer to move, resulting in more volume. Ice, on the other hand, has a maximum density of water at 4 degrees Celsius. Ice is lighter than water and has a lower density. As a result, it floats on water.
Intext Questions (Page: 9)
Question 1.- Convert the following temperature to Celsius scale:
a) 300K b) 573K
Solution:-
a) 0°C=273K
300K= (300-273)°C = 27°C
b) 573K= (573-273)°C = 300°C
Question 2.- What is the physical state of water at:
a) 250°C b) 100°C
Solution:-
a) At 250°C – Gaseous state since it is beyond its boiling point.
b) At 100°C – It is at the transition state as the water is at its boiling point. Hence it would be present in both liquid and gaseous states.
Question 3.- For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Solution:- It is due to the latent heat as the heat supplied to increase the temperature of the substance is used up to transform the state of matter of the substance; hence, the temperature stays constant.
Question 4.- Suggest a method to liquify atmospheric gases.
Solution:- It can be achieved by either increasing the pressure or decreasing the temperature, which ultimately leads to the reduction of spaces between molecules.
Intext Questions (Page: 10)
Question 1.- Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Solution:- It is because the temperature is high and less humid on a hot dry day, enabling better evaporation. High levels of this evaporation provide better cooling effects.
Question 2.- How does the water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summer?
Solution:- An earthen pot is porous in nature. These tiny pores facilitate the penetration of water and hence their evaporation from the pot surface. The process of evaporation requires energy which is contributed by water in the pot as a result of which water turns cooler.
Question 3.- Why does our palm feel cold when we put on some acetone or petrol, or perfume on it?
Solution:- Acetone, petrol, and perfume are volatile substances that evaporate when they come in contact with air. Evaporation is facilitated as it uses energy from the palm, hence leaving a cooling effect on our palms.
Question 4.- Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer rather than a cup?
Solution:- A saucer has a larger surface area than a cup, promoting quicker evaporation. Hence, the tea or milk in a saucer cools down faster.
Question 5.- What type of clothes should we wear in summer?
Solution:- In summer, it is preferred to wear light-coloured cotton clothes because light colour reflects heat and cotton materials have pores that absorb sweat, facilitating evaporation, and hence causing a cooling effect on the skin.
Exercise – (Page:- 12)
Question1.- Convert the following temperature to Celsius scale.
a) 293K b) 470K
Solution:- 0°C=273K
a) 293K= (293 – 273)°C = 20°C
b) 470K= (470 – 273)°C = 197°C
Question 2.- Convert the following temperatures to the Kelvin scale.
a) 25°C b) 373°C
Solution:- 0°C = 273K
a) 25°C = (25+273)K = 298K
b) 373°C = (373+273)K = 646K
Question 3.- Give reason for the following observations:
a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
Solution:- At room temperature, naphthalene balls undergo sublimation wherein they directly get converted from a solid to a gaseous state without having to undergo the intermediate state, i.e., the liquid state.
b) We can get the smell of perfume while sitting several metres away.
Solution:- Molecules of air move at a higher speed and have large intermolecular spaces. Perfumes comprise substances that are volatile, which scatter quickly in air, becoming less concentrated over a distance. Hence, we are able to smell perfume sitting several metres away.
Question 4.- Arrange the following in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles – water, sugar, oxygen.
Solution:- Oxygen (gas) < water (liquid) < sugar (solid)
Question 5.- What is the physical state of water at –
a) 25°C b) 0°C c) 100°C?
Solution:-
a) At 25°C, the water will be in liquid form (normal room temperature)
b) At 0°C, the water is at its freezing point, hence both solid and liquid phases are observed.
c) At 100°C, the water is at its boiling point, hence both liquid and gaseous states of water (water vapour) are observed.
Question 6.- Give two reasons to justify –
a) Water at room temperature is a liquid.
Solution:- Water persists as a liquid at room temperature since its melting point is lower than room temperature and its boiling point (100o C) is higher.
Similarly,
i) A fixed volume is occupied by a fixed mass of water.
ii) At room temperature, water does not have a fixed shape and flows to fit the container’s shape.
As a result, water is a liquid at room temperature.
b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Solution:- Because its melting and boiling points are above room temperature, an iron almirah is a solid at room temperature. In the same way,
i) An iron almirah is rigid and has a predetermined shape.
ii) Metals have a relatively high density.
As a result, at room temperature, iron almirah is a solid.
Question 7:- Why is ice at 273K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Solution:- At 273 K, ice will absorb heat energy or latent heat from the medium to overcome fusion and transform into water. As a result, ice has a greater cooling impact than water at the same temperature since water does not absorb the excess heat from the medium.
Question 8.- What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Solution:- Steam produces severe burns. It is because it is an exothermic reaction that releases a high amount of heat which it had consumed during vaporization.
Question 9.- Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing a change in its state.
Solution:- Interconversion of three states of matter:- Using temperature or pressure, any state of matter can be turned into another.
A) Solid to Liquid → Melting (or) fusion (or) liquefaction
B) Liquid to Gas → Evaporation (or) vaporization
C) Gas to liquid → Condensation
D) Liquid to Solid → Solidification
E) Solid to Gas → Sublimation
F) Gas to Solid → solidification
Give Us Your Feedback/Suggestions
- By Durgesh Pandey Sir
(Eklavya Coaching Institute)
📞 8376976688
H-2/25, Gali No-23, Kunwar Singh Nagar, Nangloi, New Delhi -110041
(Near Sarvodaya kanya Vidyalaya & ITI, Ranhaula)





















Comments
Post a Comment