Class 6 Science Chapter - 2 Components of Food, Notes, Previous Year Questions & NCERT Solutions
Class 6 Science
Chapter - 1
Components of Food
Notes, Previous Year Questions & NCERT Solutions
--Notes--
Nutrients:- The components that are needed by our body to grow, survive and carry on different daily activities.

Our food contains mainly five major kinds of nutrients namely vitamins, minerals, carbohydrates, proteins and fats. Food also contains water and dietary fibres/roughage and water which are also required by our body.

Fig. 1: Major nutrients of food
Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates main function is providing energy to the body. These are found in our food in the form of sugar and starch i.e. simple and complex carbohydrates. Example It is found in bread, potatoes etc.
Simple Carbohydrates: These are also referred to as simple sugars, containing single monosaccharide units and found in natural sources of food i.e. milk, fruits and vegetables. These carbohydrates add certain sweetness to the food. They raise the level of blood glucose quickly but are easier to break down.
Complex Carbohydrates: These are also referred to as polysaccharides, meaning they contain hundreds or thousands of such monosaccharide units. These are typically found in wheat grain, white bread, kernel and cakes. They are relatively less sweet than simple carbohydrates and also raise blood glucose level rather slowly. However, these are tougher to break down. Cellulose is present in plant cell wall. It is a complex carbohydrate. Humans cannot digest cellulose.
Test for carbohydrates: We can test whether a particular food item contains carbohydrates by pouring 2 to 3 drops of dilute iodine solution on it. If the iodine changes its colour to blue-black, then we can ascertain that the food item does, in fact, contain carbohydrates.

Fig.2: The Two Types of Carbohydrates
Proteins: Proteins performs the very essential function of helping our body grow and repair itself. These are found in food items such as milk, pulses, eggs, meat etc. Foods containing proteins are called ‘body-building’ foods.
Test for proteins: To test whether a food item contains proteins, first we need to grind it into a paste or powder form and add 10 drops of water. To this mixture when we add 2 drops of copper sulphate solution and 10 drops of caustic soda solution. After a few minutes, if the mixture turns violet, it is indicative of the presence of protein.
Fats: Fats are also responsible for providing energy to our body. In fact, they provide more energy than carbohydrates. The body uses fat as a fuel source. Fats are essential for the absorption of vitamins A, D, E and K in the body. Butter, cheese, oil are all examples of fat-rich foods.
Test for fats: To test for fats, take a small quantity of food item and wrap a piece of paper around it and proceed to crush it. After removing the paper, allow it to dry. If you see a film of an oily patch on the paper when holding it against light, it is proof that the food contains fats.
Vitamins: Vitamins help in protecting our bodies from various kinds of diseases. They also help in keeping our eyes, gums, bones and teeth in good shape. Different types of vitamins and their uses:
| Vitamin Type | Sources | Functions | Deficiency Diseases |
Vitamin A | Leafy green vegetables, oranges, carrots, Pumpkin, Soy, Sweet potatoes | Forms and helps maintain bones, skin, tissue and teeth | Color blindness, night blindness- poor visibility at night. |
Vitamin B1 (thiamine) | Dried herbs, sunflower seeds, whole grain cereals, sesame seeds, brown rice | Enables cells to turn carbohydrates into energy | Beriberi- loss of appetite, loss of weight. |
Vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | Almonds, Asparagus, bananas, green beans, wheat bran, dried spices | Maintains Body growth and RBCs i.e. Red Blood Cells | Skin disorders, Cheilosis-breaking of lips |
Vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin) | Mutton, fish, beef, lobster, clams, eggs, oysters, crab | Helps in maintenance of central nervous system and RBCs | Pale skin, lack of RBC, Less stamina and less appetite. |
Vitamin C | Fresh herbs, cauliflower, papaya, oranges, strawberries, guava | Promotes healthy gums and teeth | Scurvy i.e. gum disease (gingivitis). |
Vitamin D | Sunshine, Mushrooms, liver, fish and eggs | Necessary for the healthy development of bones and teeth | Rickets and Osteomalacia – weakening and softening of bones. |
Vitamin E | Soyabean oil, red chilli powder, pine nuts, apricots, green olives and cooked spinach | Helps in processing vitamin K and formation of RBCs | Muscle weakness and transmission problems in nerve impulses |
Vitamin K | Green leafy vegetables, Soyabean oil. | Essential for blood coagulation | Excessive bleeding from wound. |
Minerals: Minerals are used by the body to perform various functions like building strong bones, maintaining the heartbeat, making hormones etc. The major five minerals are Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Sodium and Potassium. Examples of mineral-rich foods include leafy vegetables, fish, beans etc.
| Mineral Type | Sources | Functions | Deficiency Disease |
Calcium | Tofu, Dairy products, Salmon, Cabbage, Kale and Broccoli | Essential for efficient functioning of nervous system and healthy bones | Weak bones, lower than normal bone density and stunted growth |
Phosphorous | Lean meats, grain and milk | Essential for the maintenance of acid-base balance in body | Loss of appetite, bone fragility, muscle weakness, poor physique |
Iodine | Green leafy vegetables, Seafood, iodised salt | Formation of thyroid hormone | Goitre- Enlargement of thyroid gland, mental disability. |
Sodium | Table salt, celery | Helps keep control on blood pressure | Nausea, irritability |
Iron | Whole grain, eggs, leafy vegetables and meats | Essential for haemoglobin formation in rbc. | Anaemia – weakness, fatigue, shortness of breath |

Fig.3: The five major minerals and their source foods
Dietary Fibres/Roughage: While dietary fibres do not provide any such nutrition to our bodies but nevertheless are an important component of food. They help in easy absorption of food, helps in movement of bowel and prevents constipation. It helps our body get rid of undigested food. Cereals, fruits and vegetables are some of the roughage rich foods.
Water: Water performs the essential function of absorbing nutrients from our food. It also helps in releasing waste from our body in form of sweat and urine.
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is one that contains a variety of food items providing different types of nutrients in adequate amounts necessary for maintaining good health. The diet should contain a good amount of dietary fibre and water as well.
A balanced diet includes a combination of protein-rich pulses, sprouted seeds etc. with combinations of various flours and cereals for carbohydrates and fats along with fruits and vegetables which provide the necessary vitamins and minerals.
In addition to making sure that the right amount of food is eaten, it should also be ensured that food is properly cooked so that it does not end up losing its nutrients.
Repeated washing of fruits, pulses, rice and vegetables can result in the loss of essential vitamins and minerals.
Throwing away excess water which is used for cooking vegetables can result in the loss of considerable amounts of important proteins and minerals present in them.
It’s a well-known fact that vitamin C gets destroyed in the heat while cooking.
Obesity: Obesity is a medical condition that results from excess intake of fat-rich foods. The excess fat gets accumulated to such an extent that it starts negatively affecting one’s health, well-being and the ability to carry out certain activities.
Deficiency Diseases
Deficiency: Sometimes simply getting adequate amounts of food might not be enough if the food does not contain the required nutrients in the right amounts. Prolonged usage of such nutrient-less food may result in a condition known as Deficiency.
Deficiency Diseases: Diseases that occur from the lack of an element in the diet, usually a particular vitamin or mineral are known as deficiency diseases.
A diet lacking proteins may result in skin diseases, stunted growth, diarrhoea, swelling of face and discolouration of hair.
A diet deficient in both carbohydrates and protein may hinder the growth completely and the person becomes so frail and lean that he or she might not even be able to move.
Deficiency of certain vitamins and minerals can cause diseases like scurvy, goitre, anaemia etc. as mentioned in the tables above.
Hence one must always make sure to include all nutrients in their food and drink a good amount of water to maintain a healthy body that is free from diseases.
Malnutrition
Improper intake of nutrient-rich food may lead to another condition called malnutrition or undernutrition. Without adequate intake of food, our bones become brittle, our muscles weaken and our thinking becomes foggy. In such situations, our bodies are said to become malnourished.
When there is lack of protein in our bodies, repair of wounds and an injury becomes difficult. When this is combined with inadequate intake of calories, it leads to a condition known as Protein-energy Undernutrition or malnutrition.
There are two ways in which protein-energy malnutrition manifests itself:

Fig.4: Two types of protein-energy malnutrition diseases
Kwashiorkor: People with severe protein deficiency are often at high risk of developing this disease. People in rural areas are more likely to suffer from this disease, as there is lack of protein rich food. If one often indulges in diets that are high on carbohydrates and low on protein it can lead to them showing symptoms of kwashiorkor i.e. Edema (puffy appearance due to retention of fluid), inability to gain weight and bulging of abdomen.
Marasmus: Children and young adults are more likely to develop this disease. If there is inadequate intake of both energy and protein, it tends to manifest as marasmus. Chronic diarrhoea, weight loss, dehydration and stomach shrinkage are the major symptoms of marasmus.
--- NCERT Solution ---
(Exercise)
Question 1.- Name the major nutrients in our food.
Ans:- The major nutrients in our food are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins and minerals.
The table below shows the nutrients present in some food items: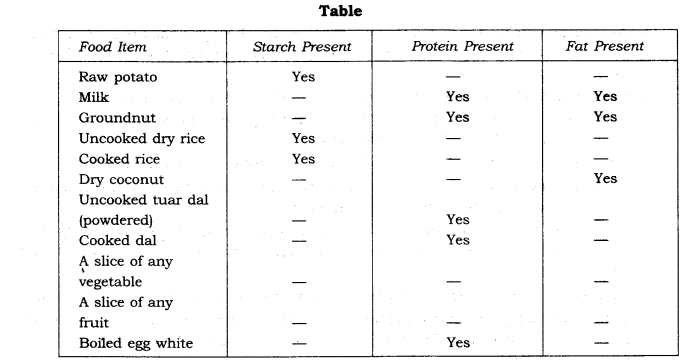
Question 2.- Name the following:
(a) The nutrients which mainly give energy to our body.
(b) The nutrients that are needed for the growth and maintenance of our body.
(c) A vitamin required for maintaining good eyesight.
(d) A mineral that is required for keeping our bones healthy.
Ans:-
a) Carbohydrates
b) Proteins
c) Vitamin A
d) Calcium
Question 3.- Name two foods each rich in:
a) Fats
b) Starch
c) Dietary fibre
d) Protein
Ans:
a) Ghee, butter,
b) Raw potato, rice,
c) Spinach, cabbage, carrot, ladies finger, (any two)
d) Milk, egg, fish, meat, pulses (any two).
Question 4.- Tick (/) the statements that are correct, cross (X) those which dire incorrect.
a) By eating rice alone, we can fulfill nutritional requirement of our body,
b) Deficiency diseases can be prevented by eating a balanced diet.
c) Balanced diet for the body should contain a variety of food items.
d) Meat alone is sufficient to provide all nutrients to the body.![]()
Question 5.- Fill in the blanks:
a) ________ is caused by deficiency of Vitamin D. ,
b) Deficiency of_________ causes a disease known as beri-beri.
c) Deficiency of Vitamin C causes a disease known as________________ .
d) Night blindness is caused due to deficiency of_______________ in our food.
Ans:
a) Rickets
b) Vitamin B1
c) Scurvy
d) Vitamin A
---- Previous Year Questions -----
Question 1.- What are nutrients? Name major nutrients.
Ans: The components of food which are needed by our body for growth and development are called nutrients. The major nutrients are:
i) Carbohydrates
ii) Fats
iii) Proteins
iv) Vitamins
v) Minerals
Question 2.- What are the functions of carbohydrates?
Ans: They complete the energy requirements of the body so they are called energy providing food.
Question 3.- Write test for detecting the presence of starch.
Ans: Take a piece of the food item. Put 2-3 drops of dilute iodine solution on it. If the colour of the food item becomes blue-black, then it indicates the presence of starch in the food item.
i) Food + Iodine — Blue-black colour (starch present)
ii) Food + Iodine — No blue-black colour (no starch present)
Question 4.- What are the functions of proteins?
Ans: Proteins are the most important nutrient. They are called body-building food. They help in the growth and repair of damaged cells and tissues of the body. They also help our body to fight against infections. Proteins make our nails, hair and muscles.
Question 5.- What are fats? Name some fat-containing substances.
Ans: The energy rich sources of food are called fats. They provide energy to the body. All types of nuts, mustard seeds, milk and butter are the major sources of fat. Like carbohydrates, fats also contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen but fats contain less oxygen than carbohydrates.
Question 6.- Write test for detecting, presence of fat.
Ans: Take small quantity of the food item. Rub it on a piece of white paper. Observe carefully, you will find that the piece of white paper shows an oily patch on it which indicates that the food item contains fat.
Question 7.- What are vitamins? Write various kinds of vitamins.
Ans: They are protective compounds with no energy value. They help in proper body functioning and are required by the body in very small quantities. Various kinds of vitamins are—Vitamin A, Vitamin B-complex, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E and Vitamin K.
Question 8.- People who eat sea-food do not suffer from Goitre. Explain.
Ans: It is so because sea-food is a rich source of Iodine and Goitre is a deficiency disease caused due to lack of Iodine.
Question 9.- Excess intake of fats is harmful for the body because it causes obesity. Would it be harmful for the body to take too much of proteins or vitamins in the diet?
Ans. Yes, excess intake of proteins and vitamins in the diet is harmful and may lead to other diseases.
Question 10.- Name the vitamin that our body prepares in the presence of sunlight.
Ans: Vitamin D.
Question 11.- Name a vitamin that is not present in milk.
Ans: Vitamin C.
Question 12.- A patient had stunted growth, swelling on face, discolouration of hair and skin disease. Doctor advised him to eat a lot of pulses, grams, egg white, milk etc. What is wrong with the patient? Explain.
Ans: The intake of protein is not enough in his diet and all these symptoms are caused due to deficiency of proteins.
Question 13.- A small child became very thin and lean and later he became so weak that he could not move. Which nutrients should he eat so as to improve his health?
Ans: Both carbohydrates and proteins.
Question 14.- What are the functions of minerals?
Ans: Minerals are protective part of foods occurring naturally and are needed by our body in small amount. Minerals are essential for proper growth of the body and to maintain good health. They do not provide energy. Milk, salt, eggs and green leafy vegetables are the main sources of minerals.
Question 15.- Write the functions of water in our body.
Ans: Water helps our body to absorb nutrients from the food. It also helps in removing the waste from the body in the form of urine and sweat. We get water from various types of liquids, fruits and vegetables.
Question 16.- What is obesity?
Ans: When a person eats too much fat-containing foods, then the fat gets deposited in his body and he may end up suffering from a condition called obesity.
Question 17.- What are deficiency diseases?
Ans: When a person eats such a food continuously for a long time which may not contain a particular nutrient, then this condition is called deficiency of that nutrient. Deficiency of one or more nutrients can cause diseases or disorders in our body. Such type of diseases are known as deficiency diseases.
Question 18.- List various types of nutrients and write the functions of each.
Ans. The various types of nutrients are:
i) Carbohydrates: They are mainly energy-providing nutrients.
ii) Fats: They provide energy for the body. They give much more energy than carbohydrates if consumed in same amount.
iii) Proteins: They are called body-building foods. Proteins help in the formation and repairing of body parts. Skin, hair, muscles, enzymes are made up of proteins.
iv) Vitamins: Vitamins help in protecting our body against disease. They also protect eyes, bones, teeth and gums.
v) Minerals: Minerals are essential for proper growth of body and to maintain good health.
Question 19.- What is a balanced diet? Write the components of balanced diet.
Ans: A diet which provides the right proportion of all the nutrients that our body needs along with roughage and water is called balanced diet. The various components of balanced diet are carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, minerals, roughage and water.
Give Us Your Feedback/Suggestions
- By Durgesh Pandey
(Eklavya Coaching Institute)
📞 8376976688, 9310533915
H-2/25, Gali No-23, Kunwar Singh Nagar, Nangloi, New Delhi -110041




Comments
Post a Comment