Class 6 Science Chapter - 4 Sorting materials Into Groups Notes, Previous Year Questions & NCERT Solutions
Class 6 Science
Chapter - 4
Sorting materials Into Groups
Notes, Previous Year Questions & NCERT Solutions
--Notes--
⏩ What is matter?
➧ Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass along with it. Objects around us are made from a different variety of materials that we see in our day-to-day life.
➧ Material is a substance that is used for making things. A material could be used to make a large number of different objects. An object could be either made of a single type of material or of many different types of materials.
⏩Properties of Materials:-
1. Appearance:- Materials can be classified on the basis of how they look or appear to be. Some materials have lustre, which is a very soft glow to them while others are plain or dull looking. Materials that have such lustre can be classified as Metals.
➧ Ex.- gold, copper, aluminium, iron etc.
➧ A metal loses its lustre after some time due to the action of moisture and air on it. Therefore only freshly-cut metals appear to have lustre on them.

2. Hardness:-
➧ Materials that can be easily compressed or scratched are called Soft.
➧ Materials that cannot be scratched and are difficult to compress are termed as Hard.
3. Soluble or Insoluble:-
➧ Materials that can be dissolved in water upon stirring are said to be soluble materials. Example, Sugar and Salt can be dissolved in water.
➧ Materials that cannot be dissolved in water no matter how much we stir them are said to be insoluble materials. Example, Stones and Clothes cannot be dissolved in water.
➧ When two liquids are mixed and it does not mix well, then it is said to be immiscible.
➧ Whereas the liquids which mix well with water are said to be miscible.

4. Objects may float or sink in water:-
There are some insoluble objects or materials which sink to the bottom of the surface when dissolved in water while some other float on the surface of the water. For Example, leaves and corks float in water while rocks and coins sink in water.

5. Transparency:-
➧ Objects or materials which can be seen through are said to be transparent objects. Example, Glass, clear water and some plastics can be seen through and are hence transparent materials.
➧ Objects and materials through which things can be seen but only partially are called Translucent objects. Butter paper and frosted glass are some examples of translucent objects.
➧ Objects which cannot be seen through are known as opaque objects. Example, Metals, wood and cardboard are some examples of opaque materials as you cannot see through them.

6 Brittle:- Those materials which break into smaller pieces or are powdered when hammered. For example, rock, glass, salt.
7 Malleable:- Materials that can be spread into thin sheets when beaten. For example, metals are malleable.
8 Ductile:- Materials that can be drawn into thin and long wires. For example, metals are ductile as well. Materials like wood, rubber, and fibres are soft.
9 Good and Bad Conductor of Electricity:-
➧ Material that allows electric current to pass through them easily is the good conductor of electricity. For example, metals are known as good conductors of electricity.
➧ Materials like wood, plastic, rubber, cork, and certain materials are bad conductors of electricity as the electric current does not pass through them.
10 Good and Bad Conductor of Heat:- All metals are good conductors of heat whereas wood is the bad conductor of heat.
11 Combustible Substances:- Those materials which catch fire on heating easily are combustible substances. For example, wood, plastic, fibre, and paper are combustible substances.
⏩Why do we need to group objects?

We need to group objects for a number of reasons:
Convenience to store: We often group objects in order to store similar objects together in order to make locating them easier in the future. Even in our homes, we store spices together in the kitchen while storing washing products in our bathrooms.
Convenience to study: We also group objects so that it becomes easy for us to study their features as well as the patterns of these features.
⏩Advantages of classification:- The several advantages of the classification of material are given below:-
a. It helps in the identification of objects.
b. It helps in the sorting of the objects.
c. It also helps in locating things when unable to find them.
d. It makes the study of different objects easy and meaningful instead of studying each material separately from each other which becomes hard.
e. It helps to understand similarities and dissimilarities between the objects around us.
***** NCERT Solution *****
Question 1.- Name five objects which can be made from wood.
Ans.-
i) Table
ii) Chair
iii) Doors
iv) Boat
v) Bed
Question 2.- Select those objects from the following which shine:-
Glass bowl, plastic toy, steel spoon, cotton shirt
Ans.- Glass bowl and steel spoon are shining objects.
Question 3.- Match the objects given below with the materials from which they could be made. Remember, an object could be made from more than one material and a given material could be used for making many objects.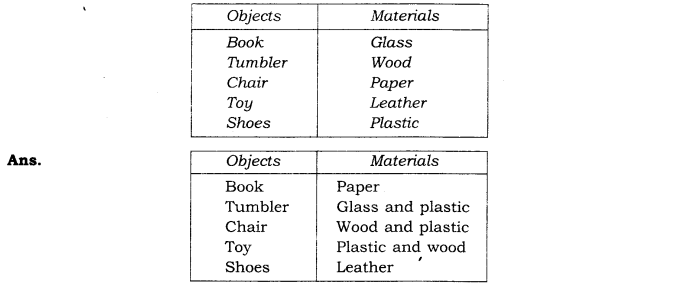
Question 4.- State whether the statements given below are ‘true’ or ‘false’.
i) Stone is transparent, while glass is opaque.
ii) A notebook has lustre while eraser does not
iii) Chalk dissolves in water.
iv) A piece of wood floats on water.
v) Sugar does not dissolve in water.
vi) Oil mixes with water.
vii) Sand settles down in water.
viii) Vinegar dissolves in water.
Ans.-
i) False
ii) False
iii) False
iv) True
v) False
vi) False
vii) True
viii) True
Question 5.- Given below are the names of some objects and materials:
Water, basket ball, orange, sugar, globe, apple and earthen pitcher Group them as:
a) Round shaped and other shapes
b) Eatables and non-eatables
Ans.-
a) i) Round shaped: Basket ball, apple, orange, globe, earthen pitcher.
ii) Other shapes: Water, sugar.
b) i) Eatables: Water, orange, sugar and apple.
ii) Non-eatables: Basket ball, globe and earthen pitcher.
Question 6.- List all the items known to you that float on water. Check and see if they will float on an oil or kerosene.
Ans.- A) List of some items that float on water:
- Paper
- Wood
- Thin plastic sheets
- Wax
- Ice
- Thermocol
- Oil
B) List of items that float on an oil:
- Paper
- Plastic sheet
- Wax
- Thermocol
- Wood
C) List of items that float on kerosene:
- Paper
- Thermocol
- Thin plastic sheet
Question 7.- Find the odd one out from the following:
a) Chair, Bed, Table, Baby, Cupboard
b) Rose, Jasmine, Boat, Marigold, Lotus
c) Aluminium, Iron, Copper, Silver, Sand
d) Sugar, Salt, Sand, Copper sulphate
Ans.-
a) Baby (all others are non-living)
b) Boat (all others are flowers)
c) Sand (all others are metals)
d) Sand (all others are soluble in water)
***** Previous Year question ******
Question 1.- Write any four properties of materials.
Ans:-
a) Appearance
b) Hardness
c) Solubility
d) Float or sink in water
e) Transparency
Question 2.- Why is a tumbler not made with a piece of cloth?
Ans:- We use tumblers made of glass, plastic and metal to keep a liquid. These substances can hold a liquid. A tumbler made of cloth cannot hold a liquid because:-
i) Cloth piece is not hard enough to hold liquids and
ii) Cloth piece has very minute pores through which the’liquid oozes out.
Question 3.- What are the similarities between iron, copper and aluminium?
Ans:-
a) They all have lustre,
b) They are all metals,
c) They are hard.
Question 4.- Mention some materials which are made up of paper.
Ans:- Books, notebooks, newspapers, toys, calendars, etc.
Question 5.- Why is water important for our body?
Ans:- Water can dissolve a large number of substances, so it is needed by the body. It is also major part of our body cells.
Question 6.- What is the basis for sorting materials?
Ans:- Materials are grouped on the basis of similarities or dissimilarities in their properties.
Question 7.- What is the reason for grouping materials?
Ans:- Materials are grouped for our convenience to study their properties and also observe any patterns in these properties.
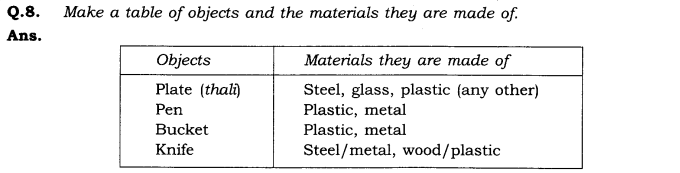
Question 9.- Make a table of different types of objects that are made from the same material.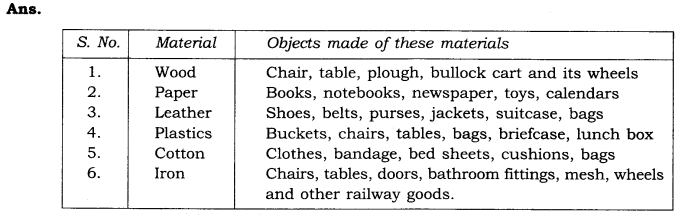
Question 10.- Make a table and find out whether the following materials mix with water: Vinegar, Lemon juice, Mustard oil, Coconut oil, Kerosene.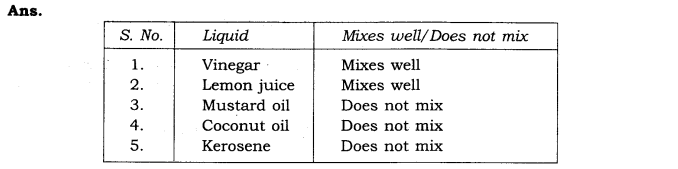
Question 11.- Metals have lustre (shine). Give reason why some metal articles become dull and loose their shine.
Ans:- Metals when exposed to air react with moisture and gases present in it, thereby forming a dull layer of some other compound on it.
Question 12.- Kerosene, coconut oil, mustard oil do not dissolve in water, even on shaking. They separate after sometime forming two different layer. Explain why.
Ans:- The molecules of water do not intermingle (mix) with the molecules of oil. The space between the molecules of water is not taken by oil, so they are immiscible in water.
Question 13.- Name a non-metal that has lustre.
Ans:- Iodine.
Question 14.- Metals generally occur in solid state and are hard. Name a metal that exists in liquid state and a metal that is soft and can be cut with knife.
Ans:- Mercury is a metal that exists in liquid state. Sodium and Potassium are soft metals and can be cut with knife.
Question 15.- Name the naturally occuring hardest substance known.
Ans:- Diamond, it is made up of carbon (non-metal).
Question 16.- Why is water called a universal solvent?
Ans:- Water dissolves a large number of substances in it. So it is called universal solvent.
Give Us Your Feedback/Suggestions
- By Durgesh Pandey
(Eklavya Coaching Institute)
📞 8376976688, 9310533915
H-2/25, Gali No-23, Kunwar Singh Nagar, Nangloi, New Delhi -110041




Comments
Post a Comment